Silver-gilt or gilded/gilt silver, sometimes known in American English by the French term vermeil, is silver (either pure or sterling) which has been gilded with gold. Most large objects made in goldsmithing that appear to be gold are actually silver-gilt; for example most sporting trophies (including medals such as the gold medals awarded in all Olympic Games after 1912 and many crown jewels are silver-gilt objects.
Silver-gilt objects have been made since ancient times across Eurasia, using a variety of gilding techniques, and a distinctive depletion gilding technique was developed by the Incas in Pre-Columbian South America. “Overlaying” or folding or hammering on gold foil or gold leaf is mentioned in Homer’s Odyssey (Bk vi, 232), and fire-gilding with mercury dates to at least the 4th century BC, and was the most common method until the Early Modern period at least, though dangerous for the workers and often caused blindness among French artisans who refined the technique in the 18th century. Today electroplating is the most commonly used method: it involves no mercury and is therefore much safer. Keum-boo is a special Korean technique of silver-gilding, using depletion gilding. In China gilt-bronze, also known as ormolu, was more common. Reference: Wikipedia
An American gilt Sterling silver figural punch bowl and laddle by George C. Shreve & Co., San Francisco, CA late 19th Century The spot hammered surface with fruiting grape leaves, two figural branch handles, each with mounted birds, gilt applied to grape leaves and bowl interior, matching ladle with figural branch and grape handle, raised on scrolled feet, height of punch bowl 10in (25.5cm); length over handles 14in (35.5cm); total weighable silver approximately 60oz troy.
Sold for US$ 16,250 (£ 12,439) inc. premium at Bonhams in 2018
Oval silver gilt medal.(obverse) Bust of Thomas Betterton, left, with long hair. Made in 1711
Reference: © The Trustees of the British Museum
A WILLIAM III SILVER-GILT CASKET MARK OF PIERRE HARACHE I, LONDON, 1695 Oblong and on four bun feet, with gadrooned borders, the sides with finely engraved panels depicting, on the front, a putto in scrolling foliage, on the sides military trophies and on the back a putto holding a cypher beneath a coronet, the hinged cover engraved with a cypher within a lozenge shaped cartouche and with coronet above, supported by a putto and with lions below, all surrounded by scrolling foliage on a matted ground, marked underneath, inside cover, on internal frame and plaque, further engraved underneath with a scratch weight ’91:9′ 10 ½ in. (16.5 cm.) wide 92 oz. (2,862 gr.)
Sold for GBP 175,000 at Christies in 2018
Russian Silver-Gilt and Enamel Icon of the Mother of God with Saints Anthony of Kiev and Theodosius of Kiev Maker’s mark I.C, possibly for Ivan Solodovnikov, Moscow, 1771 Rectangular, centering the Mother of God enthroned with the Christ Child on her lap, each with enameled halo, the border repoussé with foliate arabesques, the sides centering the saints. Height 12 1/2 inches (32 cm), width 10 1/2 inches (26.7 cm).
Sold for $6,250 (includes buyer’s premium) at Christies in 2019
A PAIR OF SILVER GILT ENAMEL FILIGREE DOUBLE GOURD
Each of double gourd form and enamelled on gilt-silver wire ground. Qing Dynasty period.
Sold for $2,900 at California Asian Art Auction Gallery USA in 2019
The Wine-Harvest Cup owes its name to its mount, which evokes the theme of wine and intoxication. Inspired by the work of sixteenth-century German goldsmiths, this piece by François-Désiré Froment-Meurice (1802-55) reflects the admiration for Renaissance art that characterized the period of the July Monarchy. Froment-Meurice showed a similar cup at the Industrial Exhibition of 1844, where it was highly praised. An iconography of intoxication The oval cup in yellow agate is supported by a mount of silver gilt in the form of a vinestock which appears rooted in a trilobate base decorated in opaque champlevé enamel. On the base sit figures personifying different forms of intoxication: the poet Anacreon (the intoxication of poetry); Lot with one of his daughters (the intoxication of love); and Noah (the intoxication of wine). From among them rises the vine, with shoots and leaves and bunches of grapes formed of pearls, which grows upward so as also to form the handle. Five putti clamber on the woody stem, on which Reason lies enfeebled in her cups. Immediately beneath her, a dramatic scene unfolds, as a nest of four young birds is attacked by a lizard – a favourite subject in the Romantic period.
Reference:The Louvre
Silver-gilt bowl,ca. 725–675 B.C. Cypriot The central tondo shows a winged deity of Assyrian type felling a rampant lion with a sword. The surrounding frieze presents a variety of animal and narrative motifs, including two specifically Egyptian subjects: a sphinx wearing the Egyptian double crown and a lion treading over a dead man, symbolizing the pharaoh dominating his enemies. The broad outer band features a variety of combats. Of greatest importance, however, are two inscriptions. At the top, above an Assyrianizing figure killing a lion, a Cypriot syllabic inscription reads, “I am [the bowl] of Akestor, king of Paphos.” It was partly obliterated and replaced by “I am [the bowl] of Timokretes,” presumably the next owner. The bowl is exceptionally significant for its excellent condition, high quality, and amalgam of Egyptian, Assyrian, and Phoenician features.
Reference: The Metropolitan Museum of Art
Silver gilt engagement ring Silver gilt Norwegian engagement finger ring, fused and engraved.
Reference: Museum of Applied Art and Sciences
Silver Gilt Snuffbox Indian, Calcutta about 1840
Reference: Museum of Fine Arts Boston
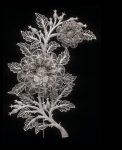
A silver-gilt belt buckle, Ottoman provinces, probably Greece, 18th/19th century composed of two slightly-curved silver plaques fitted together, surface-side gilt and richly decorated in filigree with stylised foliate scrolls and pomegranate-like details, four small hooks for fastening 18.4 by 30.2cm.
Sold for 2,750 GBP at Sothebys in 2019
Two Italian Chalices A chalice was used during the Mass to serve the consecrated wine. The form and ornament of this example are typical of a type made in large numbers in Tuscany. The finest were made entirely of silver gilt and enamel. Slightly cheaper versions, such as these, had a silver bowl and a copper-gilt foot and stem. Tuscany, Italy, dated 1365. Copper gilt, with enamelled silver mounts, the bowl of silver gilt Probably Tuscany, Italy, 1350–1400. Copper gilt, with enamelled silver mounts and silver-gilt bowl
Reference: © Victoria and Albert Museum
This magnificent brooch is an outstanding example of Lalique’s jewelry. Here, layered fern leaves, in opalescent cameo glass and green enamel, are connected by diamond-set “stalks.” At the center a large cushion-shaped opal is mounted in a silver-gilt frame set with small diamonds of varying size. The lateral segments are hinged to the central unit to permit movement. Henry Walters bought this piece from Lalique in 1904 at the World’s Fair in St. Louis, Missouri. The symmetrical design anticipates Lalique’s future work. Within several years, the artist abandoned both jewelry and the Art Nouveau style to devote himself to the production of glass molded in the Art Deco style.
Reference: The Walters Art Museum